

我拿到的開發板實際板載的?MCU?是?GD32F310G8,QFN28pin 封裝,基于?ARM?CORTEX M4 內核,主頻 72MHz, 芯片內置 64KB flash,8KB SRAM, 兩路?I2C?外設。
整體概述
首先感謝極術社區給我試用GD32開發板的機會,讓我體驗一下近幾年國產MCU開發體驗。該芯片是基于arm cortex-M4內核,主頻72Mhz,flash 64k,ram 8k,以及豐富的外設。
本次試用是一個讀取三軸加速度計的實驗,主要使用的是硬件iic。
硬件連接
傳感器介紹
SC7A20 是一款高精度 12bit 數字三軸加速度傳感器芯片,內置功能 更豐富,功耗更低,體積更小,測量更精確。
芯片通過 IC2/SPI 接口與 MCU 通信,加速度測量數據以中斷方式或 查詢方式獲取。INT1和INT2中斷管腳提供多種內部自動檢測的中斷信號, 適應多種運動檢測場合,中斷源包括 6D/4D 方向檢測中斷信號、自由落體 檢測中斷信號、睡眠和喚醒檢測中斷信號、單擊和雙擊檢測中斷信號。
芯片內置高精度校準模塊,對傳感器的失調誤差和增益誤差進行精確補償。 ±2G、±4G、±8G 和±16G 四種可調整的全量程測量范圍,靈活測量外 部加速度,輸出數據率 1HZ 和 400HZ 間可選。
軟件功能
該軟件主要使用了GD32開發板的硬件iic,外部中斷以及串口,這三部分功能,串口的配置在其他文章的當中已經有敘述,本文只主要介紹iic和外部中斷的使用.
硬件iic
初始化gpio

配置硬件iic
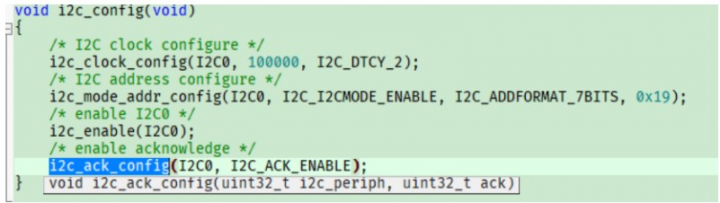
根據廠商提供的庫函數(具體參考gd32f3x0_i2c.c文件),我們可以很容易的初始化iic。剩下的就是對傳感器進行配置了,該傳感器需要配置寄存器較多,廠商直接提供了一份demo程序,只需要適配讀取寫入的接口就可以很快的使用了。
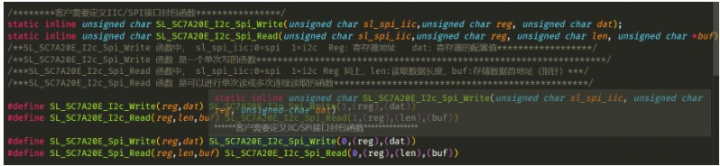
我需要做的就是把iic的讀取和寫入進行適配適配函數如下:
void I2C_LeaderWrite(uint16_t followerAddress, , uint8_t targetAddress, uint8_t *txBuff,
uint8_t numBytes) {
/* wait until I2C bus is idle */
while (i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_I2CBSY))
;
/* send a start condition to I2C bus */
i2c_start_on_bus(I2C0);
/* wait until SBSEND bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_SBSEND))
;
/* send slave address to I2C bus */
i2c_master_addressing(I2C0, followerAddress, I2C_TRANSMITTER);
/* wait until ADDSEND bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_ADDSEND))
;
/* clear ADDSEND bit */
i2c_flag_clear(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_ADDSEND);
/* wait until the transmit data buffer is empty */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_TBE))
;
for (i = 0; i < numBytes; i++) {
/* data transmission */
i2c_data_transmit(I2C0, txBuff[i]);
/* wait until the TBE bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_TBE))
;
}
/* send a stop condition to I2C bus */
i2c_stop_on_bus(I2C0);
/* wait until stop condition generate */
while (I2C_CTL0(I2C0) & 0x0200)
;
}
void I2C_LeaderRead(uint16_t followerAddress, uint8_t targetAddress, uint8_t *rxBuff,
uint8_t numBytes) {
/* wait until I2C bus is idle */
while (i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_I2CBSY))
;
/* send a start condition to I2C bus */
i2c_start_on_bus(I2C0);
/* wait until SBSEND bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_SBSEND))
;
/* send slave address to I2C bus */
i2c_master_addressing(I2C0, followerAddress, I2C_TRANSMITTER);
/* wait until ADDSEND bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_ADDSEND))
;
/* clear the ADDSEND bit */
i2c_flag_clear(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_ADDSEND);
/* wait until the transmit data buffer is empty */
while (SET != i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_TBE))
;
/* enable I2C0*/
i2c_enable(I2C0);
/* send the EEPROM's internal address to write to */
i2c_data_transmit(I2C0, targetAddress);
/* wait until BTC bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_BTC))
;
/* send a start condition to I2C bus */
i2c_start_on_bus(I2C0);
/* wait until SBSEND bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_SBSEND))
;
/* send slave address to I2C bus */
i2c_master_addressing(I2C0, followerAddress, I2C_RECEIVER);
/* wait until ADDSEND bit is set */
while (!i2c_flag_get(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_ADDSEND))
;
/* clear the ADDSEND bit */
i2c_flag_clear(I2C0, I2C_FLAG_ADDSEND);
/* while there is data to be read */
for (int i = 0; i < numBytes; i++) {
/* code */
/* read a data from I2C_DATA */
rxBuff[i++] = i2c_data_receive(I2C0);
/* send a stop condition */
i2c_stop_on_bus(I2C0);
}
/* wait until the stop condition is finished */
while (I2C_CTL0(I2C0) & 0x0200)
;
/* enable acknowledge */
i2c_ack_config(I2C0, I2C_ACK_ENABLE);
i2c_ackpos_config(I2C0, I2C_ACKPOS_CURRENT);
}
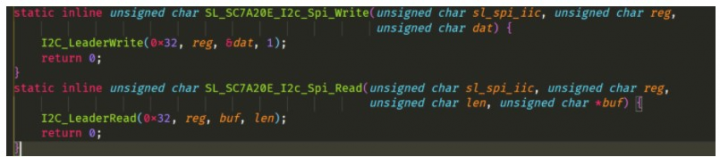
然后把這兩個函數適配:
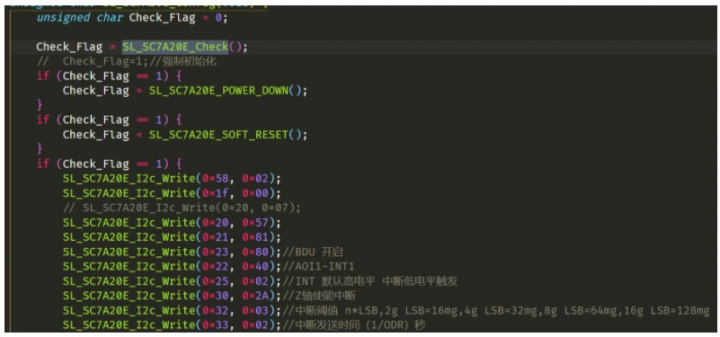
然后對傳感器進行設置
外部中斷
使用外部中斷可以使用用于喚醒mcu,這對設計低功耗的產品很有意義,當傳感器超過設定的閾值的時候,那么就會產生一個中斷來通知mcu,需要進一步的處理數據,外部中斷的配置如下所示:
void exit_wakeup_interrupt_config(void)
{
/* configure the priority group */
nvic_priority_group_set(NVIC_PRIGROUP_PRE2_SUB2);
/* enable the key wakeup clock */
rcu_periph_clock_enable(RCU_GPIOA);
rcu_periph_clock_enable(RCU_CFGCMP);
/* configure button pin as input */
gpio_mode_set(GPIOA, GPIO_MODE_INPUT, GPIO_PUPD_NONE, GPIO_PIN_0);
/* enable and set key wakeup EXTI interrupt to the higher priority */
nvic_irq_enable(EXTI0_1_IRQn, 2U, 0U);
/* connect key wakeup EXTI line to key GPIO pin */
syscfg_exti_line_config(EXTI_SOURCE_GPIOA, EXTI_SOURCE_PIN0);
/* configure key wakeup EXTI line */
exti_init(EXTI_0, EXTI_INTERRUPT, EXTI_TRIG_FALLING);
exti_interrupt_flag_clear(EXTI_0);
}
數據處理
由于我們使用的是三軸傳感器,對于姿態位置的計算并不是很精確,因此,此處只用簡單角度計算,傾角的計算原理如下
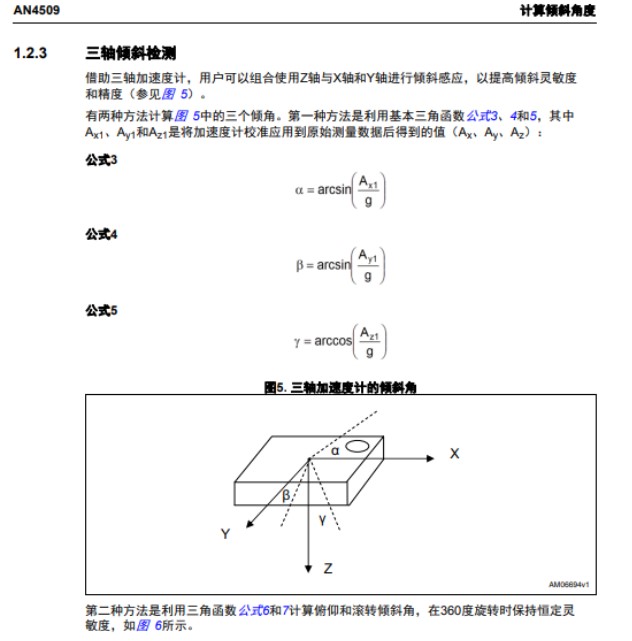
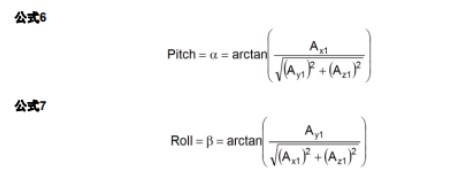
計算代碼如下:
#define DEG_TO_RAD(x) ((x) * 0.01745329252)
#define RAD_TO_DEG(x) ((x) * 57.2957795131)
void angle_calculation() {
double pitch, roll, paw;
pitch = atan(xyz_mg[X] / sqrt(pow(xyz_mg[Y], 2) + pow(xyz_mg[Z], 2)));
roll = atan(xyz_mg[Y] / sqrt(pow(xyz_mg[X], 2) + pow(xyz_mg[Z], 2)));
paw = atan(sqrt(pow(xyz_mg[X], 2) + pow(xyz_mg[Y], 2)) / xyz_mg[Z]);
printf("[RAD]pitch:%.2f | roll:%.2f | paw:%.2f rn", pitch, roll, paw);
printf("[DEG]pitch:%.2f° | roll:%.2f° | paw:%.2f° rn", RAD_TO_DEG(pitch), RAD_TO_DEG(roll),
RAD_TO_DEG(paw));
}